from tvbo import Dynamics, SimulationExperiment
from IPython.display import Markdown
lorenz = Dynamics(
parameters={
"sigma": {"value": 10.0},
"rho": {"value": 28.0},
"beta": {"value": 8 / 3},
},
state_variables={
"X": {"equation": {"rhs": "sigma * (Y - X)"}},
"Y": {"equation": {"rhs": "X * (rho - Z) - Y"}},
"Z": {"equation": {"rhs": "X * Y - beta * Z"}},
},
)
code = SimulationExperiment(local_dynamics=lorenz).render_code('jax')The Virtual Brain Ontology
Welcome to tvbo!
tvbo is a Python library for defining, simulating, and analyzing dynamical systems in computational neuroscience. It combines ontology-driven knowledge representation with flexible simulation capabilities.
Core Features: - - Load: Access curated models and studies from the knowledge database - Specify: Define dynamical systems and network models with simple specification language - Build: Configure brain network models - Generate: Produce optimized simulation code (Python, JAX, Julia) - Share: Export reproducible models with standardized metadata
![]()
Quickstart
pip install tvboFor more installation options, see the Installation Guide.
name: LorenzAttractor
parameters:
sigma:
value: 10
label: Prandtl number
rho:
label: Rayleigh number
value: 28
beta:
value: 2.6666666666666665
state_variables:
X:
equation:
lhs: \dot{X}
rhs: sigma * (Y - X)
Y:
equation:
lhs: \dot{Y}
rhs: X * (rho - Z) - Y
Z:
equation:
lhs: \dot{Z}
rhs: X * Y - beta * Zoutput:
Markdown("```python" + code + "```")
from collections import namedtuple
import jax.scipy as jsp
import jax
from tvbo.data.types import TimeSeries
from tvbo.utils import Bunch
import jax.numpy as jnp
def cfun(weights, history, current_state, p, delay_indices, t):
n_node = weights.shape[0]
a, b = p.a, p.b
x_j = jnp.array([
])
pre = x_j
pre = pre.reshape(-1, n_node, n_node)
def op(x): return jnp.sum(weights * x, axis=-1)
gx = jax.vmap(op, in_axes=0)(pre)
return b + a*gx
def dfun(current_state, cX, _p, t, local_coupling=0):
sigma, rho, beta = _p.sigma, _p.rho, _p.beta
# unpack coupling terms and states as in dfun
X = current_state[0]
Y = current_state[1]
Z = current_state[2]
# compute internal states for dfun
return jnp.array([
sigma*(Y - X), # X
-Y + X*(rho - Z), # Y
X*Y - Z*beta, # Z
])
def integrate(state, weights, dt, params_integrate, delay_indices, external_input):
"""
Heun Integration
================
"""
t, _ = external_input
noise = 0
params_dfun, params_cfun, params_stimulus = params_integrate
history, current_state = state
stimulus = 0
cX = jax.vmap(cfun, in_axes=(None, -1, -1, None, None, None), out_axes=-
1)(weights, history, current_state, params_cfun, delay_indices, t)
dX0 = dfun(current_state, cX, params_dfun, t)
X = current_state
# Calculate intermediate step X1
X1 = X + dX0 * dt + noise + stimulus * dt
# Calculate derivative X1
dX1 = dfun(X1, cX, params_dfun, t)
# Calculate the state change dX
dX = (dX0 + dX1) * (dt / 2)
next_state = current_state + (dX)
return (history, next_state), next_state
def g(dt, nt, n_svar, n_nodes, n_modes, seed=0, sigma_vec=None, sigma=0.0, state=None):
"""Standard Gaussian white noise using xi ~ N(0,1).
Returns (nt, n_svar, n_nodes, n_modes): sqrt(dt) * sigma * xi.
- sigma_vec: optional per-state sigma (length n_svar).
- sigma: scalar fallback when sigma_vec is None.
- state: optional current state placeholder for future correlative noise.
"""
key = jax.random.PRNGKey(int(seed))
xi = jax.random.normal(key, (nt, n_svar, n_nodes, n_modes))
if sigma_vec is not None:
sigma_b = jnp.asarray(sigma_vec)[None, ..., None, None]
else:
sigma_b = jnp.asarray(sigma)
noise = jnp.sqrt(dt) * sigma_b * xi
return noise
def monitor_raw(time_steps, trace, params, t_offset=0):
dt = 0.01220703125
return TimeSeries(time=(time_steps + t_offset) * dt, data=trace, title="Raw")
def transform_parameters(_p):
sigma, rho, beta = _p.sigma, _p.rho, _p.beta
return _p
c_vars = jnp.array([]).astype(jnp.int32)
def kernel(state):
# problem dimensions
n_nodes = 1
n_svar = 3
n_cvar = 3
n_modes = 1
nh = 1
# history = current_state
current_state, history = (state.initial_conditions.data[-1], None)
ics = (history, current_state)
weights = state.network.weights_matrix
dn = jnp.arange(int(n_nodes)) * \
jnp.ones((int(n_nodes), int(n_nodes))).astype(jnp.int32)
idelays = jnp.round(state.network.lengths_matrix /
state.network.conduction_speed.value / state.dt).astype(jnp.int32)
di = -1 * idelays - 1
delay_indices = (di, dn)
dt = state.dt
nt = state.nt
time_steps = jnp.arange(0, nt)
# Generate batch noise using xi with per-state sigma_vec.
# Prefer state-provided sigma_vec (supports vmapped sweeps); fallback to experiment-level constants.
seed = getattr(state.noise, 'seed', 0) if hasattr(
state.noise, 'seed') else 0
try:
sigma_vec_runtime = getattr(state.noise, 'sigma_vec', None)
except Exception:
sigma_vec_runtime = None
sigma_vec = sigma_vec_runtime if sigma_vec_runtime is not None else jnp.array([
0., 0., 0.])
noise = g(dt, nt, n_svar, n_nodes, n_modes, seed=seed, sigma_vec=sigma_vec)
p = transform_parameters(state.parameters.local_dynamics)
params_integrate = (p, state.parameters.coupling, state.stimulus)
def op(ics, external_input): return integrate(ics, weights,
dt, params_integrate, delay_indices, external_input)
latest_carry, res = jax.lax.scan(op, ics, (time_steps, noise))
trace = res
trace = jnp.hstack((
trace[:, [0], :],
trace[:, [1], :],
trace[:, [2], :],
))
t_offset = 0
time_steps = time_steps + 1
labels_dimensions = {
"Time": None,
"State Variable": ['X', 'Y', 'Z'],
"Space": ['0'],
"Mode": ['m0'],
}
return TimeSeries(time=(time_steps + t_offset) * dt, data=trace, title="Raw", sample_period=dt, labels_dimensions=labels_dimensions)from tvbo import Dynamics, SimulationExperiment
lorenz = Dynamics(
parameters={
"sigma": {"value": 10.0},
"rho": {"value": 28.0},
"beta": {"value": 8 / 3},
},
state_variables={
"X": {"equation": {"rhs": "sigma * (Y - X)"}},
"Y": {"equation": {"rhs": "X * (rho - Z) - Y"}},
"Z": {"equation": {"rhs": "X * Y - beta * Z"}},
},
)
SimulationExperiment(local_dynamics=lorenz).run(duration=1000).plot()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tvbo import Network
from tvbo import SimulationExperiment, Dynamics
from tvbo import Coupling
from tvboptim.types import GridAxis, Space
from tvboptim.execution import ParallelExecution
import jax
import bsplot
c = Coupling.from_ontology("HyperbolicTangent")
sc = Network(
parcellation={"atlas": {"name": "DesikanKilliany"}},
normalization={"rhs": "(W - W_min) / (W_max - W_min)"},
)
exp = SimulationExperiment(
local_dynamics=Dynamics.from_ontology("Generic2dOscillator"),
network=sc,
coupling={"name": "Linear", "parameters": {"a": {"value": 1}}},
integration={
"method": "Heun",
"duration": 3000,
"step_size": 0.1,
},
)
model = exp.execute("jax")
state = exp.collect_state()
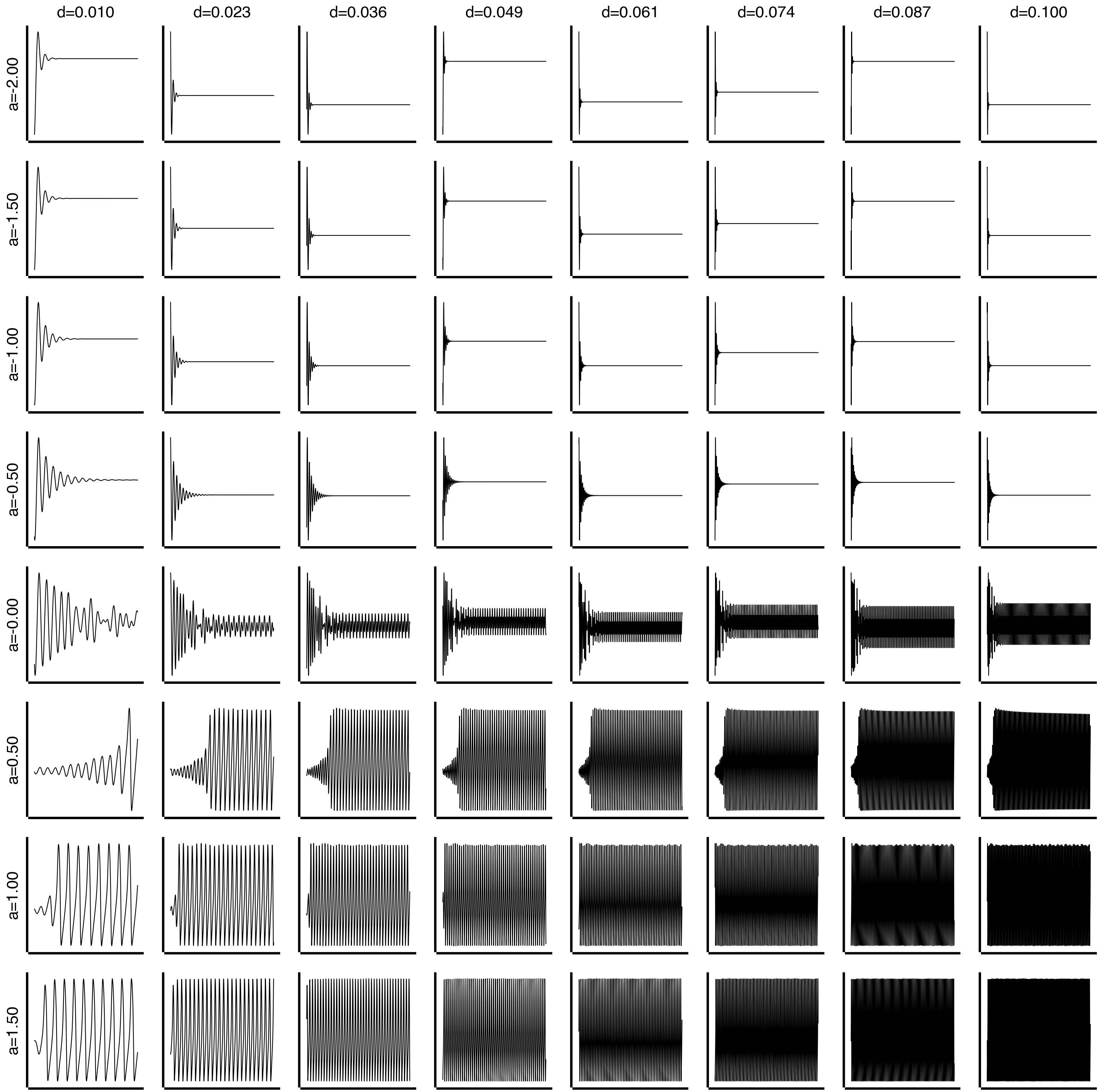
n = 8
# Explore a (controls Hopf bifurcation) and d (time scale separation)
# a ~ 0 is the bifurcation point; d controls fast/slow dynamics
state.parameters.local_dynamics.a = GridAxis(-2, 1.5, n)
state.parameters.local_dynamics.d = GridAxis(0.01, 0.1, n)
grid = Space(state, mode="product")
n_devices = jax.device_count()
def explore():
exec = ParallelExecution(model, grid, n_pmap=n_devices, n_vmap=10)
return exec.run()
exploration_results = explore()
print(exploration_results.results.shape)
# Reshape: (n_pmap, n_vmap, time, state_vars, nodes, modes) -> (n_combinations, time, state_vars, nodes)
data = exploration_results.results.data.squeeze() # remove modes dim
# Flatten n_pmap and n_vmap dimensions
data = data.reshape(-1, *data.shape[2:]) # (n_pmap*n_vmap, time, state_vars, nodes)
# Get parameter values directly from the grid (no redundant linspace!)
axis_vals = grid._generate_axis_values()
a_vals = axis_vals.parameters.local_dynamics.a
d_vals = axis_vals.parameters.local_dynamics.d
fig, axs = plt.subplots(n, n, figsize=(12, 12))
for i in range(min(n * n, data.shape[0])):
row, col = i // n, i % n
ax = axs[row, col]
# data[i] has shape (time, state_vars, nodes) - plot first state variable, first node
ax.plot(data[i, 1000:, 0, 0], linewidth=0.5)
# Labels: rows = a (first axis), cols = d (second axis)
if row == 0:
ax.set_title(f"d={d_vals[col]:.3f}", fontsize=10)
if col == 0:
ax.set_ylabel(f"a={a_vals[row]:.2f}", fontsize=10)
bsplot.style.format_fig(fig)
for ax in fig.axes:
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])(8, 8, 30000, 2, 87, 1)